THE PLANT, THE HERB,
DE HERBORIST
One of the best natural resources on our planet.
What, how and when
Cannabis Sativa L. has been considered taboo since the beginning of the last century, but finally this plant is gradually coming back into the spotlight. Because Cannabis has so many different application methods and uses, De Herborist’s mission is to contribute to the rediscovery of this plant.
There are more than 200 uses for this plant from medicinal to industrial.We work mainly with the raw plant material such as leaves, stems, seeds and flowers. All our products are carefully extracted by our CGMP Certified lab, from oil to concentrate.
A quick overview of our most used ingredients
Hemp seed oil comes from the small seeds of the Cannabis sativa plant. The seeds do not contain the same levels of compounds as the plant itself, but they have a rich profile of other nutrients, fatty acids, and other useful bioactive compounds. Since hemp seed oil contains no cannabinoids, it is not psychoactive. The production of CBD oil uses the stalks, leaves, and flowers of the hemp plant, which contain a higher concentration of CBD, another potentially beneficial compound in the plant.
The oil from the hemp seed is highly nutritious and may be especially helpful for the skin. The vitamins and fatty acids in this oil may help keep the skin healthy and prevent breakouts, protect it from inflammation, oxidation, and other causes of aging. Although these initial results look promising, scientists need to carry out studies in humans to confirm the benefits of this oil.
The fatty acid content of hemp seed oil may also be good for the brain, which requires plenty of healthful fats to operate properly.
A 2014 review Trusted Source concludes that an increase in alpha-linolenic acid, one of the fatty acids in hemp oil, appears to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. This fatty acid, which doctors call linolenic acid, is also present in fish oils and flaxseed oil. However, the researchers call for more clinical trials to confirm these results.
This amber and viscous cannabidiol intensive oil is derived from Cannabis sativa L. leaves of cultivars listed in the EU Plant variety database with earthy smell and taste with notes of pine and pepper.
This preparation contains naturally present decarboxylated phytocannabinoids (50% w/w), terpenes (0.5% w/w) and waxes (2% w/w), all within hemp seed oil for standardization of content. It dissolves in a similar range of solvents to the powdered products. In the EU Cosmetics Ingredients Database, Cannabis leaf extract CBT oil is indicated as useful as an emollient and for skin conditioning.
With a similar appearance, flavors and specifications to the CBD oil, this leaf extract oil is rich in cannabigerol (CBG), which is also indicated for cosmetics use an emollient and as a skin conditioner.
Cannabinoids are compounds found in cannabis. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid
tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) (Delta9-THC or Delta8-THC), the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis. Cannabidiol (CBD) is another major constituent of the plant. At least 113 distinct cannabinoids have been isolated from cannabis.
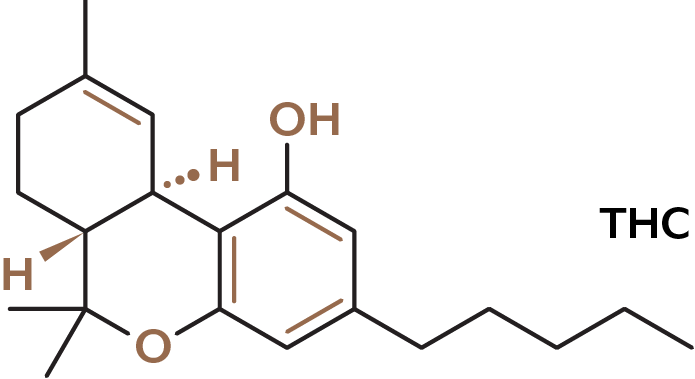
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the principal psychoactive constituent of cannabis and one of at least 113 total cannabinoids identified in the plant. Although the chemical formula for THC (C21H30O2) describes multiple isomers, the term THC usually refers to the Delta-9-THC isomer with chemical name (−)-trans-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. Like most pharmacologically active secondary metabolites of plants, THC is a lipid found in cannabis, assumed to be involved in the plant’s evolutionary adaptation.
All our products never exceed the legal limits of THC around the world!
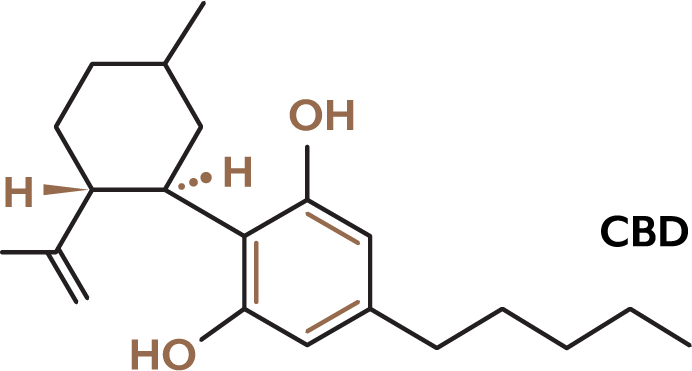
Cannabidiol (CBD) is a phytocannabinoid discovered in 1940. It is one of 113 identified cannabinoids in cannabis plants, along with tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), and accounts for up to 40% of the plant’s extract. As of 2019, clinical research on CBD included studies related to anxiety, cognition, movement disorders, and pain, but there is insufficient high-quality evidence that cannabidiol is effective for these conditions.
Cannabidiol does not appear to have any intoxicating effects (i.e., “getting high”) such as those caused by ∆9-THC in Cannabis, but it is under preliminary research for its possible anti-anxiety and anti-psychotic effects.
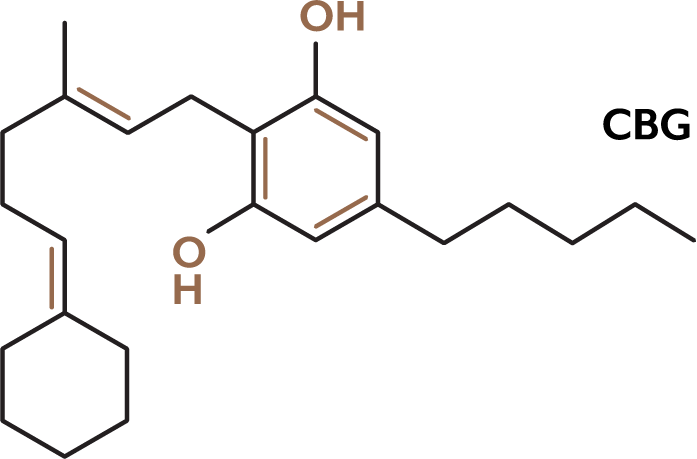
Cannabigerol (CBG) is one of at least 113 identified cannabinoid compounds found in the plant genus Cannabis. Cannabigerol is the decarboxylated form of cannabigerolic acid, the parent molecule from which other cannabinoids are synthesized. Cannabigerol is a minor constituent of cannabis. During plant growth, most of the cannabigerol is converted into other cannabinoids, primarily tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) or cannabidiol (CBD), leaving about 1% cannabigerol in the plant.
Terpenes are a class of natural products consisting of compounds with the formula (C5H8)n. Comprising more than 30,000 compounds, these unsaturated hydrocarbons are produced predominantly by plants, particularly conifers. Terpenes are further classified by the number of carbons: monoterpenes (C10), sesquiterpenes (C15), diterpenes (C20), etc. A well known monoterpene is alpha-pinene, a major component of turpentine.
Monoterpenes are a class of terpenes that consist of two isoprene units and have the molecular formula C10H16. Monoterpenes may be linear (acyclic) or contain rings (monocyclic and bicyclic). Modified terpenes, such as those containing oxygen functionality or missing a methyl group, are called monoterpenoids. Monoterpenes and monoterpenoids are diverse. They have relevance to the pharmaceutical, cosmetic, agricultural, and food industries.
Sesquiterpenes are a class of terpenes that consist of three isoprene units and often have the molecular formula C15H24. Like monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes may be acyclic or contain rings, including many unique combinations. Biochemical modifications such as oxidation or rearrangement produce the related sesquiterpenoids.
Sesquiterpenes are found naturally in plants and insects, as semiochemicals, e.g. defensive agents or pheromones.
Flavonoids (or bioflavonoids; from the Latin word flavus, meaning yellow, their color in nature) are a class of polyphenolic secondary metabolites found in plants, and thus commonly consumed in the diets of humans.
Chemically, flavonoids have the general structure of a 15-carbon skeleton, which consists of two phenyl rings (A and B) and a heterocyclic ring (C, the ring containing the embedded oxygen).This carbon structure can be abbreviated C6-C3-C6. According to the IUPAC nomenclature, they can be classified into:
The three flavonoid classes above are all ketone-containing compounds and as such, anthoxanthins (flavones and flavonols).This class was the first to be termed bioflavonoids. The terms flavonoid and bioflavonoid have also been more loosely used to describe non-ketone polyhydroxy polyphenol compounds, which are more specifically termed flavanoids. The three cycles or heterocycles in the flavonoid backbone are generally called ring A, B, and C. Ring A usually shows a phloroglucinol substitution pattern.
Live terpenes are composed of only botanical-derived terpenes, which capture the aromatic peak point of the cannabis plant. Just before harvesting, the cannabis aromatic peak point of the untouched terpene profile expresses its most pure and pungent flavors.
Palate terpenes brings together terpenes, ketones and esters to deliver diverse sensations.
By amplifying the hidden tastes of cannabis and incorporating new botanical ingredients, Palate terpenes introduces appealing and immersive flavors, holding the “whole-plant” experience.
Terpene profiles are the complex assembly of mono & sesquiterpenes, defining the unique characteristics of a plant.
Free delivery in Belgium!
Free returns within 14 days

We are available Monday – Friday

100% Secure payments
De Herborist is one of the first Belgian developers that offers ecological and natural well-being, selfcare and lifestyle products made from cannabis and its compounds.
Email usStay up to date with our products, offers and events!
Support your local shop and think twice before ordering online! It’s more ecologic friendly and there might be a shop in your neighbourhood where they provide tailored advice and guidance on our products!
DE HERBORIST
Broekstraat 154D
9220 Hamme, Belgium
BE0714.939.389